In modern water treatment, automation isn’t just an upgrade—it’s essential.
As industries demand precise, consistent, and hands-free operation, automated RO (Reverse Osmosis) systems using PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) and SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) are quickly becoming the gold standard.
Automation delivers:
- Consistent water quality
- Enhanced system safety
- Real-time visibility
- Reduced downtime and operating costs
In this guide, you’ll learn how PLC and SCADA integrate in RO systems, why automation matters, and how it transforms industrial water management.
1. Why Automation Matters in RO Water Systems
RO plants involve multiple stages—feedwater pumping, pre-filtration, membrane processing, flushing, and post-treatment.
Without automation, you risk:
- Human error
- TDS/flow inconsistencies
- Unnoticed failures
- Excess energy and chemical use
Automation ensures:
- Continuous parameter monitoring (TDS, pressure, flow)
- Smart control of pumps, valves, and dosing systems
- Safety interlocks and alarms
- Data logging for compliance and optimization
Need help upgrading from manual to automated RO? [Talk to our automation specialists →]
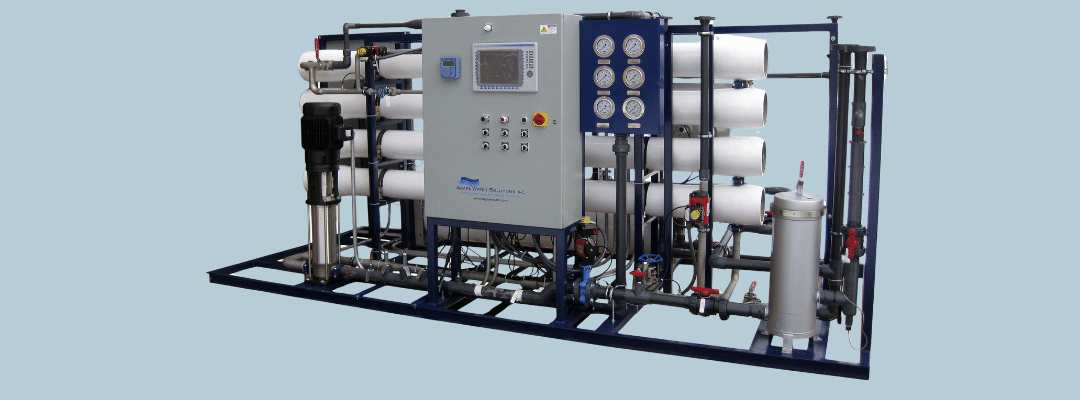
2. What Is a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller)?
A PLC is a rugged industrial controller that automates electro-mechanical processes.
In RO systems, it acts as the system’s brain, taking sensor input and executing logic to control devices.
Key PLC Functions in RO Plants:
- Auto Start/Stop: Based on tank levels or quality thresholds
- Auto Flushing: Timed membrane rinse cycles
- Pressure/Flow Monitoring: Keeps processes within optimal ranges
- Dry Run/Overpressure Protection: Prevents equipment damage
- Chemical Dosing Logic: Antiscalant, pH, chlorine control
- Alarm Triggers: Alerts for TDS spikes, power loss, low pressure
Example: When the permeate TDS > 150 ppm, PLC initiates membrane flushing and sends an alert to SCADA.
3. What Is SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition)
SCADA is a software system that visualizes, monitors, and controls the RO plant in real time.
It connects to the PLC and displays data on HMI panels, computers, or even mobile dashboards.
Core SCADA Capabilities:
- Real-time display: TDS, pH, flow, pressure, temp, recovery
- Process mimic diagrams for operator clarity
- Data logging & trend analysis for audits
- Alarm logs and remote fault alerts (email/SMS)
- Remote control via Ethernet, cloud, or IoT gateways
PLC controls the plant, SCADA visualizes and optimizes it.
4. PLC–SCADA Integration Architecture
A typical automated RO system includes:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Sensors | TDS, pressure, flow, level, pH, temp |
| Actuators | Pumps, valves, dosing pumps |
| PLC | Processes sensor input, executes logic |
| SCADA/HMI | Visualizes plant, logs data, issues alerts |
| Protocols | Modbus, Profibus, Ethernet/IP |
Example Workflow:
- Operator sets target TDS = 100 ppm
- PLC monitors conductivity
- TDS > 100 → Auto flush triggered
- SCADA logs it + notifies via alarm
5. Key Automation Features in Modern RO Plants
| Feature | Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Auto Start/Stop via Tank Sensors | Controls pumps when levels change | Cuts manual effort and overflows |
| Auto Membrane Flushing | Periodic rinsing | Extends membrane lifespan |
| PID-Based Flow/Pressure Loops | Real-time flow control | Stabilizes plant performance |
| TDS/Conductivity Monitoring | Ensures output quality | Prevents non-compliant water |
| Alarm & Fault Indication | Alerts for breakdowns | Minimizes downtime |
| Data Logging & Trending | Tracks critical parameters | Enables preventive maintenance |
| SCADA Remote Access (Mobile/Desktop) | Full control from anywhere | Improves reliability & convenience |
6. Benefits of Automation in RO Systems
Consistent Water Quality
Closed-loop control ensures stable output within quality limits.
Reduced Downtime
Fault detection and alarms reduce breakdown-related delays.
Energy & Chemical Efficiency
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) and smart dosing reduce energy and chemical use by up to 30%.
Operator Safety
Automatic shutdowns and interlocks prevent dry runs, pressure surges, and other hazards.
Real-Time Analytics
SCADA logs performance trends, aiding audits and ISO documentation.
Remote Monitoring
View, adjust, or stop your system from anywhere via mobile dashboard or cloud SCADA.
7. Where Automation Is Used
- Pharma/Biotech – WFI & purified water
- Food & Beverage – Ingredient water precision
- Hospitals & Hotels – Centralized water management
- Power Plants – Boiler feed automation
- Industrial Plants – Utility/process water
- Municipal RO & STP Plants – 24×7 remote control
8. Emerging Trends in RO Automation
- IoT-Enabled SCADA: Access from cloud dashboards
- AI Optimization: Adaptive control based on water trends
- Energy-Saving VFD Integration: Dynamic pump control
- Cybersecure SCADA: Hardened access for remote systems
- Digital Twin Simulations: Train operators & optimize virtually


Recent Comments