Grey water refers to relatively clean wastewater that comes from household sources such as sinks, showers, baths, washing machines, and dishwashers. Unlike black water (from toilets), grey water typically contains fewer harmful contaminants and is therefore more suitable for recycling and repurposing. Grey water can be reused for various purposes, especially for non-potable uses (water that is not meant for drinking).
Sources of Grey Water
- Showers and baths: Water containing soap, shampoo, and dirt from the body.
- Bathroom sinks: Water with soap, toothpaste, and small amounts of dirt.
- Laundry: Water with detergents and softeners.
- Kitchen sinks: Grey water from kitchen sinks is usually avoided for reuse due to the presence of grease, food particles, and oils, which can make it harder to treat.
Benefits of Repurposing Grey Water
- Water Conservation: Repurposing grey water helps conserve freshwater by reducing the need for potable water in non-essential uses.
- Reduces Water Bills: Reusing grey water can significantly reduce household or commercial water bills by cutting down on the amount of clean water used for irrigation, toilet flushing, etc.
- Environmentally Friendly: Reduces the load on septic systems or municipal treatment plants, minimizing water pollution and energy consumption associated with wastewater treatment.
- Sustainability: Provides a sustainable water management practice, especially in areas facing water scarcity.
How Grey Water Can Be Repurposed
1. Irrigation for Gardens and Landscaping
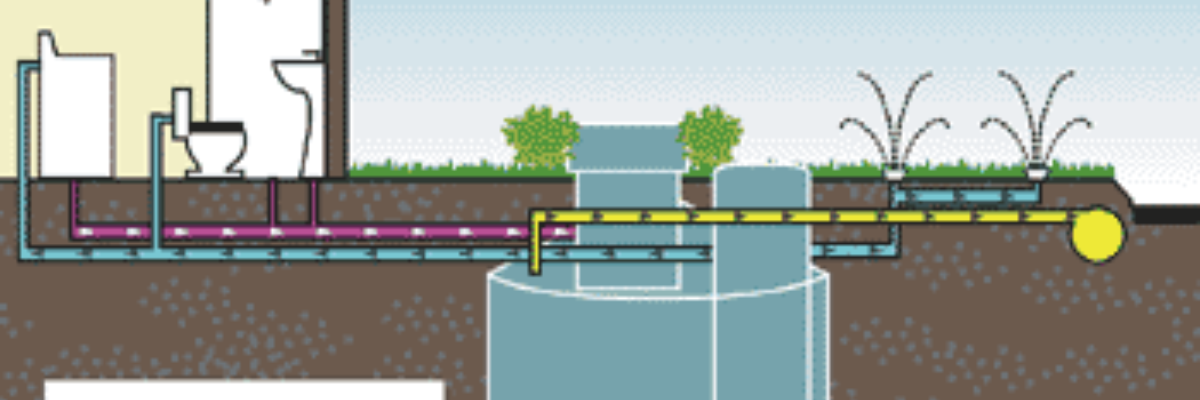
- Primary Use: Grey water is most commonly repurposed for irrigation. Plants can safely use grey water if the right types of detergents and soaps are used (those without harmful chemicals like sodium or boron, which can damage plants).
- Drip Irrigation Systems: Grey water is ideal for subsurface or drip irrigation systems that water plants directly at the root level, minimizing evaporation.
- Precautions: Use grey water for non-edible plants like shrubs, trees, and lawns. For vegetable gardens, it’s safer to use grey water only for fruit trees or to avoid direct contact with edible parts.
2. Toilet Flushing
- Significant Water Savings: Toilets consume a large amount of potable water. Grey water can be collected and used to flush toilets, reducing the amount of clean water used.
- How It Works: Systems can be installed that treat and store grey water for use in toilets. The water is usually filtered to remove large particles before being pumped into the toilet tank.
3. Cooling Systems and Industrial Use
- Cooling Towers: In industrial or commercial buildings, grey water can be treated and reused in cooling towers, reducing the need for clean water in these systems.
- Factory Processes: Many industries can use treated grey water in processes where high water quality is not required, such as for cleaning or cooling machinery.
4. Dust Suppression
- Construction Sites: Grey water can be used for dust suppression in construction areas or on unpaved roads. This reduces the need for potable water in activities where water is simply sprayed to control dust.
5. Car Washing
- Grey water can be reused for car washing at home or in commercial car washes where recycled water systems are in place. This reduces the demand for freshwater, which is especially valuable in water-scarce areas.
6. Fire Suppression
- In some areas, grey water can be stored and used for fire suppression. While potable water is not necessary for putting out fires, grey water can provide an alternative water source.
7. Reuse in Washing Machines
- Some grey water systems can be set up to reuse lightly contaminated water from the final rinse cycle of washing machines for the next washing load’s pre-rinse, reducing water usage.
Grey Water Treatment Options
Grey water should be treated to some extent before reuse, especially if it will be stored or used in systems like irrigation or toilet flushing. Untreated grey water can become stagnant and lead to foul smells or promote bacterial growth. There are several treatment methods available:
1. Filtration
- Basic Filtration: Removes large particles like hair, dirt, and soap scum. Simple filters like mesh or screen filters can be used at the collection point.
- Advanced Filtration: Multi-stage filtration systems may include sand filters, gravel filters, or charcoal filters to remove finer particles and organic material.
2. Settling Tanks
- Grey water can be directed to a settling tank where heavier particles settle to the bottom, and cleaner water rises to the top. The cleaner water can then be drained and reused.
3. Biofiltration
- Biofilters use living plants, bacteria, and microbes to break down contaminants in grey water. Systems like constructed wetlands or grey water gardens can treat grey water naturally as it moves through soil and plant roots.
4. Disinfection
- UV Light: Ultraviolet light can disinfect grey water by killing bacteria and viruses without using chemicals.
- Chlorination: In some systems, chlorine is added to grey water to disinfect it before reuse. However, this is less common for small-scale residential use.
- Ozone Treatment: Ozone generators can be used to disinfect grey water, breaking down organic matter and killing pathogens.
5. Grey Water Recycling Systems
- Specialized systems can be installed in homes or commercial buildings to automatically filter, disinfect, and pump grey water for reuse in toilets or irrigation.
Challenges and Considerations
- Health and Safety: While grey water is generally safe for reuse, there is always a risk of bacteria and pathogens if the water is not treated or used properly. It is important to avoid direct human contact, especially if using untreated grey water.
- Regulations: The reuse of grey water is regulated in many places, and local laws may require specific treatment levels, permits, or system approvals.
- Soap and Detergent Selection: Not all soaps and detergents are safe for grey water reuse, particularly for irrigation. Using biodegradable, phosphate-free, and low-sodium products ensures that grey water is safe for plants.
- Storage Issues: Grey water should not be stored for long periods as it can become stagnant and start to smell. It’s best to reuse grey water immediately or treat it if long-term storage is needed.
Conclusion
Grey water is a valuable resource that can be repurposed for various non-potable uses, significantly reducing freshwater consumption. By treating and reusing grey water for tasks like irrigation, toilet flushing, and even industrial applications, households and businesses can conserve water, reduce water bills, and promote sustainable practices.


Recent Comments